Heel Pain
The heel is a cushion of fatty tissue that protects the structures of the foot, including the heel bone, muscles and ligaments. Heel pain is a common foot complaint commonly presenting in plantar fasciitis, heel spurs, bursitis and nerve impingements . Sever's disease is a common cause of heel pain in children.
Common causes of heel pain include one or more of the following
- Abnormal walking style (gait), such as rolling the feet inwards
- Obesity
- Poor footwear
- Plantar muscle tear
- Standing, running or jumping on hard surfaces
- Injury to the heel, such as stress fractures
- Bursitis (inflammation of a bursa)
- Neuroma (nerve enlargement)
- Nerve impingement.
Plantar Fasciitis
The plantar fascia is a band of connective tissue that runs along the sole from the heel to the ball of the foot. One of its main roles is to keep the bones and joints in position during weight bearing . Bruising, over loading and tearing the plantar fascia will commonly cause inflammation and heel pain which is often difficult to treat without the help of your podiatrist and physiotherapist. Commonly heel pain is often worse first thing in the morning or after rest or after sitting for long periods of time
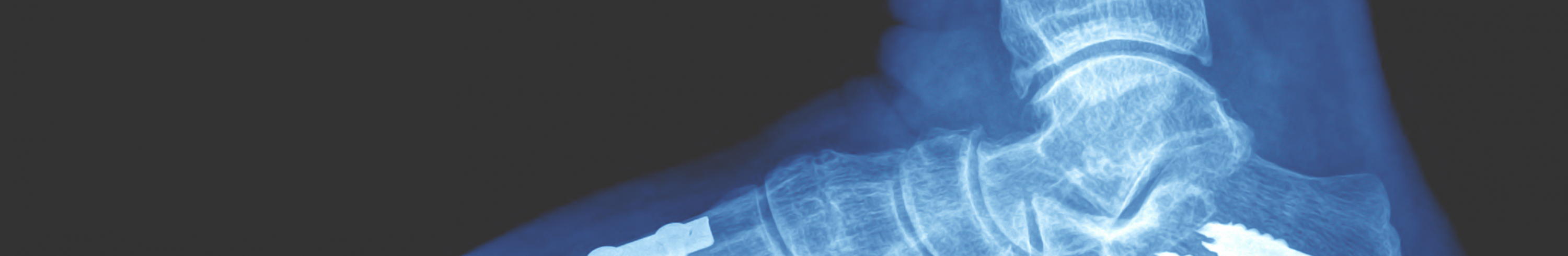
Heel spur
A foot which functions abnormally will often place extra strain on the plantar fascia crfeating a point of pressure which may develop chronic inflammation and possibly lead to a bony growth or spur. The spur can only be seen on x-ray, but its presence is often flagged by a tender patch at the heel on the sole of the foot. You may have heel spurs without realising it - it is estimated that about one in 10 Australians have heel spurs without any symptoms. The spur itself does not cause the pain, but pain may be associated with inflammation in the area.
Treatment for Heel pain usually involves a combination of the following modalities
- Flexibility/strengthening exercises
- Ultrasound therapy
- Anti-inflammatory medicine (topical or oral)
- Correct muscle imbalances (usually calf muscle inflexibility)
- Custom made flexible and cushioned orthoses to help support the foot